Class aptent sociosqu ad litora torquent per conubia nostra, per inceptos himenaeos. In tempus, erat eget tincidunt elementum mauris quam laoreet erat.

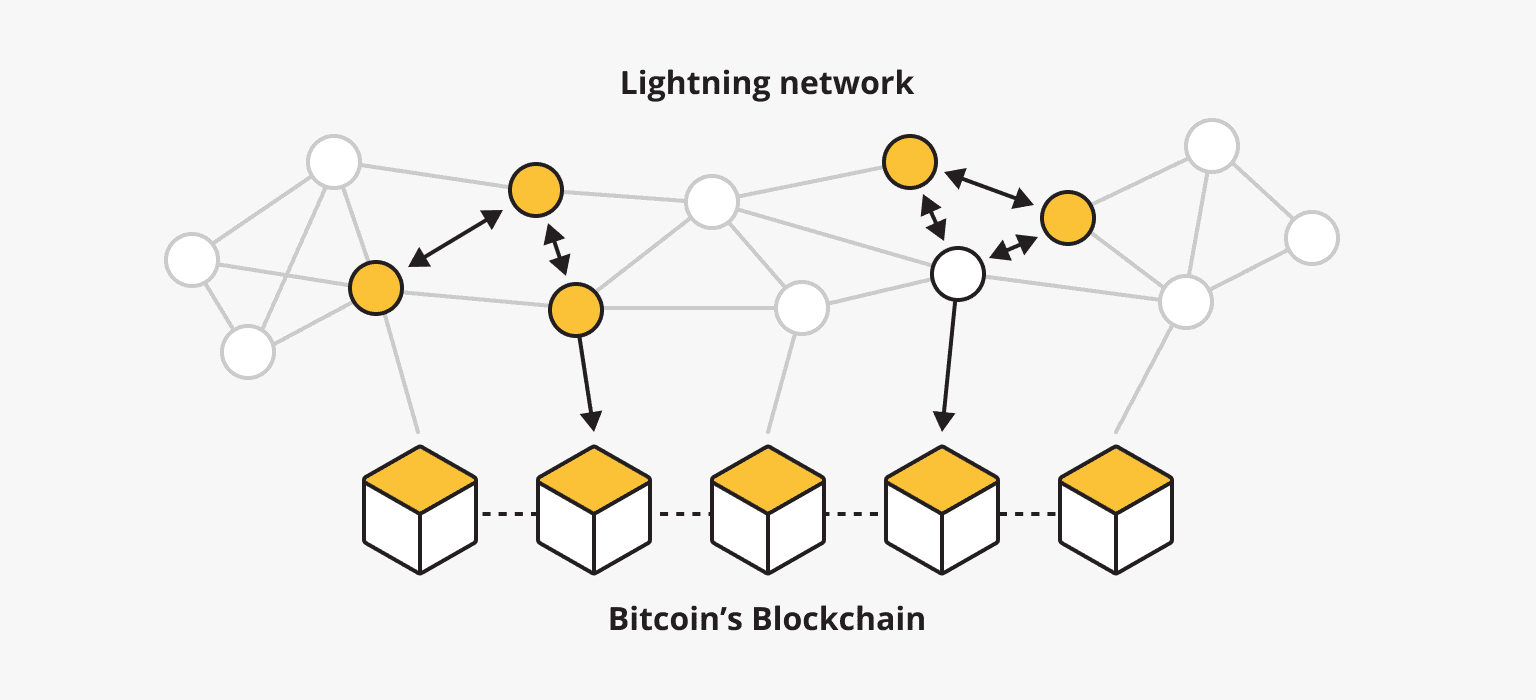
The Bitcoin Lightning Network is a “layer 2” technology designed to make Bitcoin transactions faster and cheaper by moving them off the main blockchain. Here are some key points about it:
Speed and Cost: It allows for instant payments with very low fees, making it ideal for small transactions or micropayments12.
Scalability: The network can handle millions to billions of transactions per second across the network, significantly more than the Bitcoin blockchain itself2.
Security: Transactions are secured by blockchain smart contracts, ensuring that they are safe and reliable2.
Use Cases: It’s used for various applications, including tipping on social media platforms like Twitter, enabling cross-border payments, and more1.
How does the Lightning Network work?
The Lightning Network works by creating a second layer on top of the Bitcoin blockchain, allowing for faster and cheaper transactions. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it operates:
Opening a Channel: Two parties open a payment channel by creating a multi-signature wallet, which requires both parties to sign off on transactions. They deposit a certain amount of Bitcoin into this wallet12.
Transacting Off-Chain: Once the channel is open, the two parties can conduct an unlimited number of transactions between themselves without broadcasting each transaction to the Bitcoin blockchain. These transactions are recorded off-chain12.
Updating Balances: Each transaction updates the balance of the multi-signature wallet. Both parties keep a copy of the updated balance sheet, ensuring they agree on the current state of the channel12.
Closing the Channel: When the parties are done transacting, they close the channel. The final balance is then broadcast to the Bitcoin blockchain, and the funds are distributed accordingly12.
Routing Payments: The network can route payments through multiple channels. For example, if Alice wants to pay Charlie but doesn’t have a direct channel with him, the payment can be routed through Bob, who has channels with both Alice and Charlie12.
This system allows for near-instantaneous transactions with minimal fees, making it ideal for small or frequent payments.
How do I set up a Lightning wallet?
Setting up a Lightning wallet is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
Choose a Wallet: Select a Lightning wallet that fits your needs. Some popular options include BlueWallet, Phoenix, Muun, and Wallet of Satoshi12.
Download and Install: Download the wallet app from your device’s app store and install it.
Create a New Wallet:
Open the app and follow the prompts to create a new wallet.
Securely back up your recovery phrase (usually 12 or 24 words). This is crucial for recovering your wallet if you lose access to your device.
Fund Your Wallet:
To start using the Lightning Network, you need to fund your wallet with Bitcoin. You can do this by transferring Bitcoin from another wallet or purchasing Bitcoin directly within the app if it supports this feature12.
Open a Payment Channel:
Some wallets automatically open a payment channel when you receive your first Lightning payment. Others may require you to manually open a channel. Follow the wallet’s instructions for this step12.
Start Transacting:
You can now send and receive payments using the Lightning Network. Use QR codes or Lightning invoices to make transactions12.
Can you explain how routing works in more detail?
Certainly! Routing in the Lightning Network is a fascinating process that allows payments to be sent between parties who do not have a direct payment channel with each other. Here’s a detailed look at how it works:
1. Network of Channels
The Lightning Network consists of a web of interconnected payment channels. Each channel is a direct connection between two parties who have locked up some Bitcoin in a multi-signature wallet.
2. Finding a Path
When you want to send a payment to someone you don’t have a direct channel with, the network finds a path through the existing channels. This path is a series of hops from one node (user) to another until it reaches the recipient.
3. Routing Algorithm
The Lightning Network uses a routing algorithm to find the most efficient path. This algorithm considers factors like channel capacity, fees, and the reliability of nodes. The goal is to find a path that can handle the payment amount and has the lowest fees.
4. Onion Routing
To ensure privacy, the Lightning Network uses a technique called onion routing. Here’s how it works:
The sender encrypts the payment information in multiple layers, like an onion.
Each node along the path peels off one layer to find out where to send the payment next.
This way, no single node knows the entire path, only the next hop, preserving the privacy of the transaction.
5. HTLCs (Hashed Timelock Contracts)
Payments are secured using HTLCs, which ensure that the payment is either completed or refunded. Here’s the process:
The sender creates a hash of a secret and sends it along with the payment.
Each node along the path locks the payment with the hash.
The recipient must reveal the secret to unlock the payment.
If the secret is not revealed within a certain time, the payment is refunded to the sender.
6. Fees
Each node that forwards the payment can charge a small fee. These fees are usually much lower than Bitcoin transaction fees on the main blockchain, making the Lightning Network cost-effective for small transactions.
Example, Imagine Alice wants to pay Charlie, but she doesn’t have a direct channel with him. However, Alice has a channel with Bob, and Bob has a channel with Charlie. The payment can be routed through Bob:
- Alice sends the payment to Bob.
- Bob forwards the payment to Charlie.
- Charlie receives the payment and reveals the secret to unlock it.
- This process happens almost instantaneously, allowing for quick and efficient transactions.
Would you like to know more about any specific part of this process?
How do nodes find each other in the Lightning Network?
Nodes in the Lightning Network find each other through a process called “gossiping,” which involves sharing information about the network’s topology. Here’s a detailed look at how it works:
1. Gossip Protocol
Nodes use a gossip protocol to share information about the network. This protocol allows nodes to broadcast their existence and the channels they have opened with other nodes. This information includes:
- Node IDs (public keys)
- Channel IDs
- Channel capacities
- Node addresses (IP addresses)
2. Node Discovery
When a new node joins the network, it connects to a few known nodes (often called “bootstrap nodes”)
3. Building a Network Map
As nodes receive gossip messages, they build a local map of the network’s topology. This map helps them understand which nodes are connected and the capacity of each channel.
4. Finding Routes
When a node needs to send a payment, it uses its local network map to find a route to the destination.
The routing algorithm considers factors like channel capacity, fees, and the reliability of nodes to find the most efficient path12.
5. Connecting to Peers
Nodes can also manually connect to specific peers by using their public keys and IP addresses.
Example
Imagine you set up a new node and connect it to a few bootstrap nodes. These nodes start sending you gossip messages about other nodes and channels. Your node builds a map of the network, and when you want to send a payment, it uses this map to find the best route.
Would you like to know more about setting up a node or any specific part of this process?